It’s easy to get confused about who is a worker and who isn’t these days. Your CEO may worker longer hours than you, not the top-hatted capitalist of the Monopoly board he. Indeed, it may seem that the leisure class of the turn of the last century has been replaced by the workaholic professional and managerial class of today. Yet, if everyone is a worker and no one is a capitalist, then how can we still be living under capitalism?
The short answer is we can’t…or, better yet, we are, which means that not everyone can be a worker, no matter how hard they try and how many hours they put in. These reflections are a continuation of something I just posted on the Progressive Economics Forum. With all the talk these days in Canada about income inequality and the shrinking middle class, I thought it might be a good idea to take another look at the labour share of income. I concluded that post with the following chart.
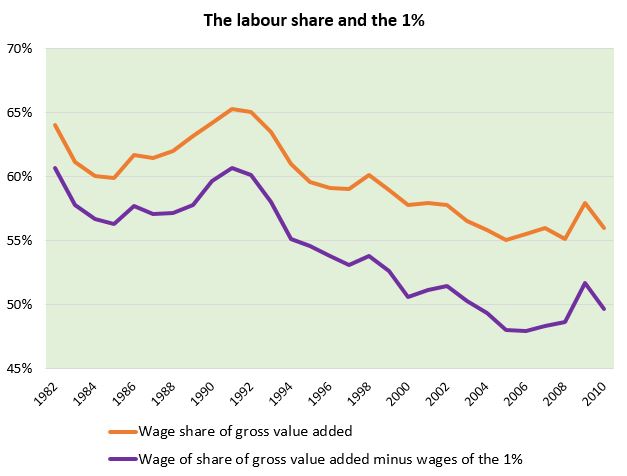
I think this has some of the answers as to why it is unhelpful to talk about the very highest income earners as workers. The reason is economic power, for which the labour share of income is a proxy. The widening gap between the income share made up by total employment income and the employment income of the bottom 99% shows precisely a gap in power. The highest earners disproportionately affect the power of labour, but they do so not as uber-workers but as something different entirely.