I’ve been meaning to post something on a chart from a Fraser Institute report for a while but slept on it. The chart comes from Fraser’s annual Consumer Tax Report and is supposed to show the different paths taken by how much households pay in taxes and how much they spend on basic goods like food and housing. 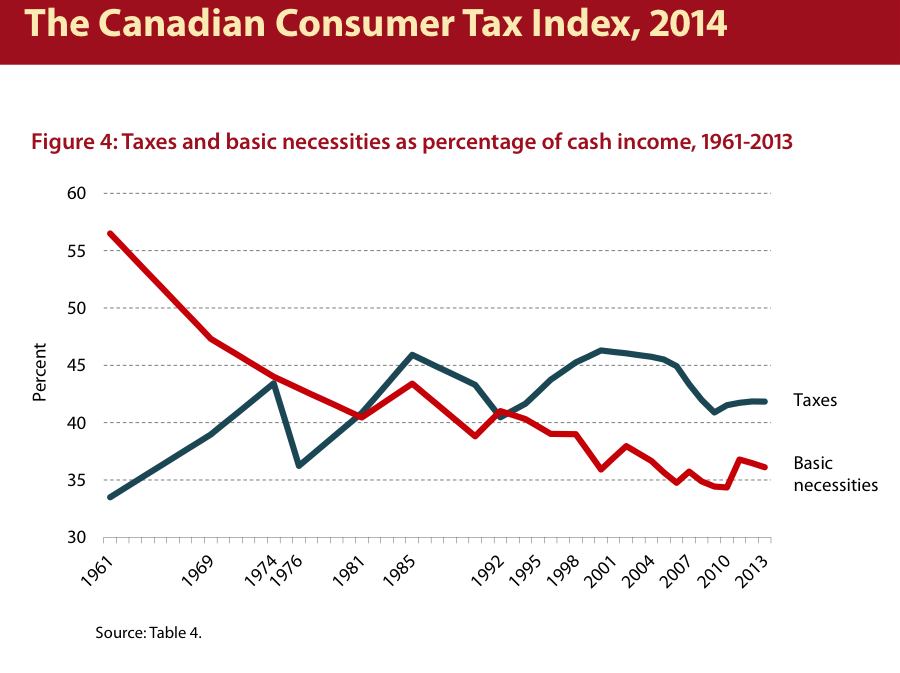
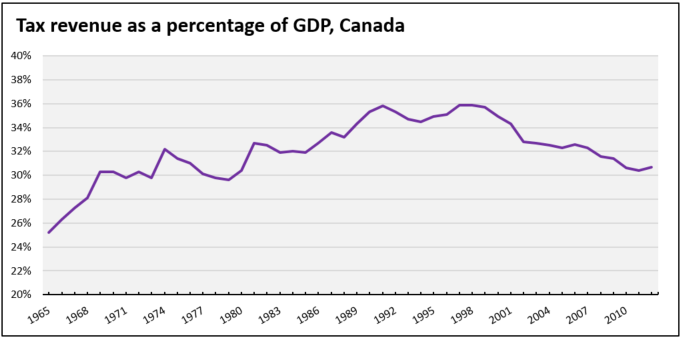
In one way, this chart represents a good news story for the right. Capitalism is fulfilling one of its major promises: the cost of the basic goods is decreasing relative to household budgets – in the aggregate, which given an increasingly unequal distribution of income means that many budgets feel this very differently. Not only that, but the welfare state is slowly shrinking. Looking closely at the chart (showing the Fraser Institute’s version of the data), we see that the relative tax take is falling since about the turn of the millennium. Of course, the chart is riddled with errors (in short, the Fraser Institute either uses too many taxes or too little income in its measures) but better OECD data shows roughly the same trend, at least for taxes.
Ironically, while a story about lower spending on necessities could be a success story (capitalism works!), of course, that’s not the point of the exercise. Instead, the chart is intended to incite anger about taxes. The big caveat being to ignore the services these taxes actually pay for: the much-lower tax bill from 50 or 60 years ago is before universal healthcare, the Canada Pension Plan and other major elements of Canada’s welfare state. Yet in its ideological fervour, the Institute might be on the right track, because what the chart shows is in fact not just a success story but the changing nature of consumption. It illustrates how what economists once called the “subsistence wage” – where subsistence is not like a fixed number of calories, square feet and so on but culturally-relative and so varies according to time and place – has changed: most strikingly, what part of consumption is privately-provided and what part is socialized and provided by the state.